Published on: 05/09/2023 · Last updated on: 13/08/2025
Introduction
There are a number of different approaches to designing online and blended courses and the one you choose may come down to personal preference but, at the heart of all models is the the need to develop effective learning which makes appropriate use of the technologies available. These are just some examples:
- The TPACK framework
- ADDIE Model
- ABC Learning Design
- 7Cs of Learning Design
- The Conversational Framework
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
- SAMR
- enABLe
TPACK framework
The TPACK framework builds on the work of American Educational Psychologist, Lee Shulman, who developed the idea of Pedagogical Content Knowledge in the 1980s. Koehler and Mishra bring these ideas into the 21st century by incorporating technological knowledge into their framework.
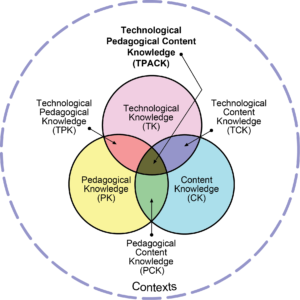
Reproduced by permission of the publisher, © 2012 by tpack.org
Listen to Punya Mishra, one of the original TPACK authors, introducing the framework:
The ADDIE Model
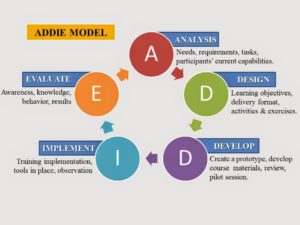
The ADDIE model has been around since the mid-1970s and is an approach to instructional/learning design, involving a number of phases:
- Analysis
- Design
- Development
- Implementation
- Evaluation
ABC Learning Design
The team from UCL has developed a series of resources, the ABC Toolkit, which you can download from their website to run your own ABC Learning Design workshop (you will need to register first). Alternatively, you can find out more about the ABC approach on our overview page.
The Conversational Framework
The Conversational Framework builds on the idea of teaching as a dialogue and is useful whether designing for face-to-face or online situations. It identifies six main learning types:
7Cs of Learning Design Framework
The 7Cs of Learning Design framework is a set of resources specifically for designing technology-enhanced learning. It combines work from the Open University and the University of Leicester. The 7Cs are:
- Conceptualise
- Capture
- Create
- Communicate
- Collaborate
- Consider
- Consolidate
Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
There are 3 main principles of Universal Design for Learning:
- engagement
- representation
- action and expression
By following these principles, learning opportunities can be designed that are flexible and fair and, most importantly, give all learners the opportunity to succeed.
A simple overview of UDL is provided in this video:
SAMR
The SAMR Model was devised by Dr R Puentedura and explores ways of using digital technologies to support and transform teaching and learning. The four steps or stages are:
- Substitution
- Augmentation
- Modification
- Redefinition
The first two stages can enhance the learning experience but do not require a fundamental shift in thinking; the last two stages can lead to transformation and real change in the learning and teaching environment.
enABLe
enABLe is a framework, developed by Portsmouth University, designed to encourage a course team approach to learning design. It is based on the University’s principles of active blended learning:
- Active – underpinned by student-centred activities
- Emphasis on context over content
- Scaffolding of learning
- Synchronous and asynchronous (rather than f2f vs online)
- Teaching well is the starting point for the meaningful adoption of technology.
The enABLe approach brings course teams together in workshops and provides a structured and collaborative approach to design resources and activities.
Further reading
- Approaches to learning design – JISC
- Learning Designer User Guide
- Back to Basics: What is ADDIE?
- ABC Learning Design
- Designing programmes and modules with ABC curriculum design
- Universal Design for Learning
- The enABLe approach
References
Ferrell, G. Smith, R. & Knight, S. (2018). Designing learning and assessment in a digital age. JISC
Koehler, M. J., & Mishra, P. (2009). What is technological pedagogical content knowledge? Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education, 9(1), 60-70
Shulman, L.S. (1986). Those who understand: Knowledge growth in teaching. Educational Researcher, 15(2), 4-14.
Kurt, S. “ADDIE Model: Instructional Design,” in Educational Technology, August 29, 2017
Laurillard, D. (2012). Teaching as a Design Science: Building Pedagogical Patterns for Learning and Technology. New York and London: Routledge.
Young, C. and Perović, N., 2016. Rapid and creative course design: as easy as ABC?. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 228, pp.390-395.
Conole, G. and Wills, S., 2013. Representing learning designs–making design explicit and shareable. Educational Media International, 50(1), pp.24-38.
Hai-Jew S. (2019) Thinking About the Learning Design: Theories, Models, Frameworks, and Heuristics. In: Designing Instruction For Open Sharing. Springer, Cham